Our Origin
1960s
Dr. Arthur Guyton starts mathematical analysis of integrative physiology (Millhorn and Guyton, 1965).

1970s
Over the next 10 years, Guyton and colleagues (1972) developed a model of cardiovascular physiology. Guyton used the 1972 model to test a variety of physiological hypotheses, mainly focusing on acute and chronic blood pressure control and the role of the kidney in the long term regulation of blood pressure.
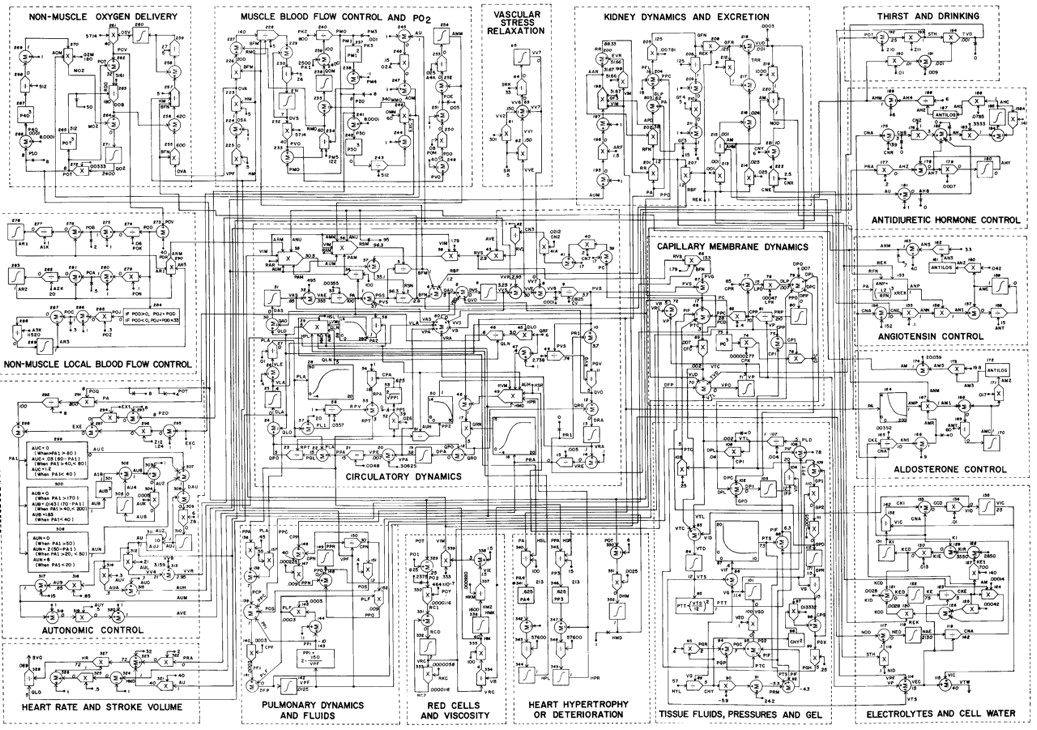
Hall, John E. (2004, November). The pioneering use of systems analysis to study cardiac output regulation. American Journal of Physiology–Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology, 287(5). Retrieved May 30, 2012, from http://ajpregu.physiology.org/content/287/5/R1009
1980s
In 1983, with the advent of the personal computer, Coleman and Randall developed a model of human physiology called Human (1983).

Image obtain from Wikipedia.
1990s
Human was expanded into a Windows software package called Quantitative Circulatory Physiology (QCP).
QCP was limited. All the physiological descriptions were written in C and compiled into an executable. But there was a way to make the physiology more accessible. With the help of Dr. Robert Hester, Dr. Coleman created...

2000s
HumMod – The most complete, mathematical model of human physiology ever created.
